一、概述
代码是解决问题的工具。当通过编码方式解决一个问题时,通常有如下步骤:
- 定义问题
- 设计解决方案
- 编码实现方案
- 测试程序
编码实现通常是我们利用计算机高级语言书写的,符合一定逻辑的程序代码,这种含逻辑的代码计算机是无法理解的,它能理解的只是一条条由0和1组成的指令即机器语言。所以这就涉及从高级语言到机器语言的翻译和转换过程,处理这个过程的程序叫编译器。
编译器这个程序,很庞大很复杂,为了让它简洁,好控制,我们把它拆成四个部分:
- 预处理器
- 编译器
- 汇编器
- 链接器
每一个阶段基本上都是在为下一个阶段做准备,它的过程如下图所示:
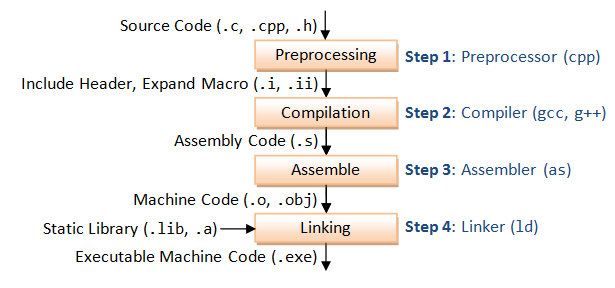
预处理器(Preprocessor)处理代码的过程叫预处理阶段,它所做的工作包括:
- #define宏定义展开
- 处理条件编译指令
- 处理#include指令
- 删除注释
- 添加行号
- 保留#pragma指令
编译器(Compiler)处理代码的过程叫编译,它主要是将上一步的产物转换成汇编代码,它的工作内容包括:
- 词法分析
- 语法分析
- 语义分析
- 优化
汇编器(Assembler)处理代码的过程叫汇编过程,它主要将汇编代码转换成二进制的机器码
- 汇编码到机器码的翻译
链接器(Linker)处理代码的过程叫链接过程,多个文件合并成一个文件
- 空间与地址分配-相同部分合并
- 符号解析和重定位-合并后位置(偏移量)调整
综上可知,目标文件是程序未链接前的一个中间文件。目标文件内容的存储方式符合ELF文件标准,所以他是一种特殊的ELF文件。
二、文件结构解析
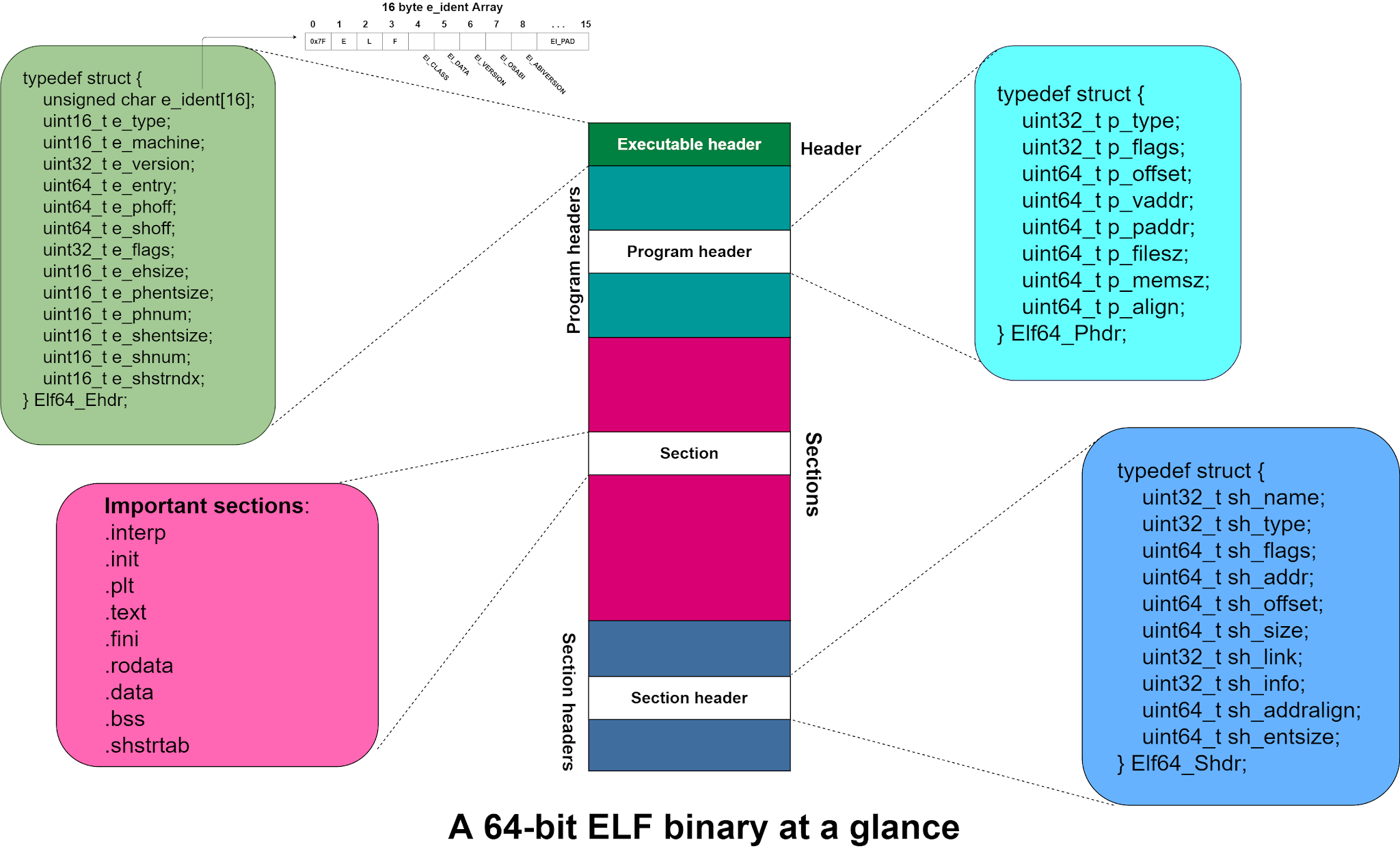
目标文件其实是ELF文件的一种,常见的ELF文件还有.so和.oat文件等。ELF文件存在两种观察角度,分别是编译角度和运行角度。编译角度是指,在代码编译阶段的存储格式。运行角度是指,文件被加载进内存时的存储格式。
两个角度看到的结构略有差异。如图:
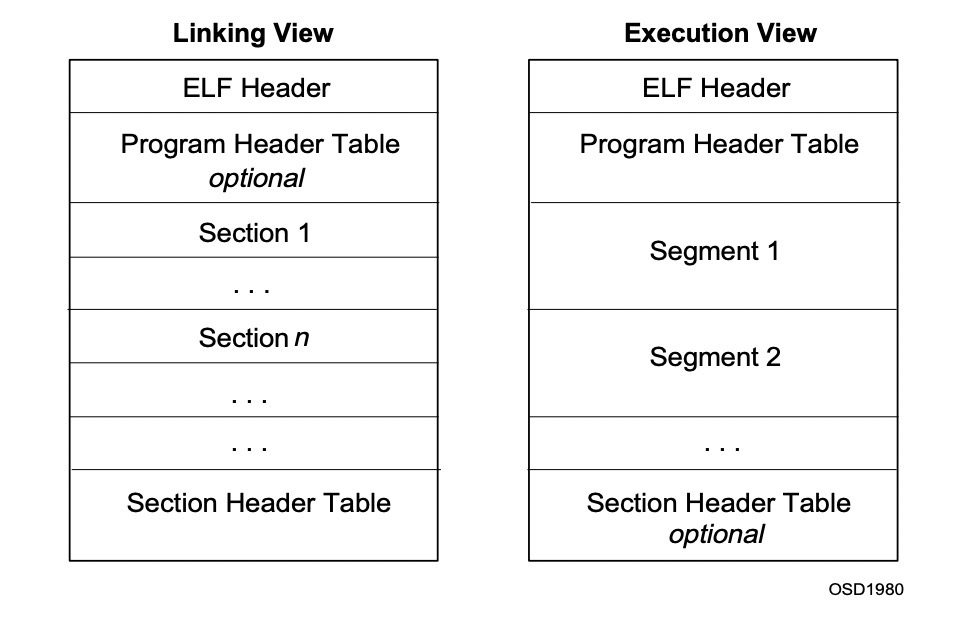
从图中可以得到这样一些信息:
1、Program Header Table对于编译视图是可选的,因为它只在程序被加载进内存时使用到。Section Header Table对于执行视图是可选的。
2、编译视图是以section为组织单位,执行视图是以segment为组织单位(多个section会被映射到同一个segment)。
下面介绍一些重要的结构。
ELF Header-文件的总体结构
1 | #define EI_NIDENT 16 |
| 文件类型 | 类型描述 |
|---|---|
| ET_NONE | 未知类型。这个标记表明文件类型不确定,或者还未定义。 |
| ET_REL | 重定位文件。 ELF 类型标记为 relocatable 意味着该文件被标记为了一段可重定位的代码,有时也称为目标文件。可重定位 目标文件通常是还未被链接到可执行程序的一段位置独立的代码 (position independent code)。 在编译完代码之后通常可以看到一 个.o 格式的文件, 这种文件包含了创建可执行文件所需要的代码 和数据。 |
| ET_EXEC | 可执行文件。ELF 类型为 executable,表明这个文件被标 记为可执行文件。这种类型的文件也称为程序,是一个进程开始执 行的入口。 |
| ET_DYN | 共享目标文件。ELF 类型为 dynamic,意味着该文件被标记 为了一个动态的可链接的目标文件,也称为共享库。这类共享库会在 程序运行时被装载并链接到程序的进程镜像中。 |
| ET_CORE | 核心文件。在程序崩溃或者进程传递了一个 SIGSEGV 信 号(分段违规)时,会在核心文件中记录整个进程的镜像信息。可以 使用 GDB 读取这类文件来辅助调试并查找程序崩溃的原因。 |
file /bin/bash //executable
file /xxx/xx.so //shared object
Program Header Table
程序装载时,根据此结构的信息对文件进行分段(segment)。描述了磁盘上可执行文件的内存布局以及如何映射到内存中。
1 | typedef struct { |
| p_flags | 描述 |
|---|---|
| PF_X | An executable segment. |
| PF_W | A writable segment. |
| PF_R | A readable segment. |
Section Header Table
用于定位文件中所有的section,主要用于链接和调试,没有Section Header Table程序仍然可以正常运行,因为它没有对内存布局进行描述,它是一个元素为Elf32_Shdr的数组结构。
1 | typedef struct |
| Section type | 描述 |
|---|---|
| SHT_NULL | This value marks the section header as inactive. It does not have an associated section. Other members of the section header have undefined values. |
| SHT_PROGBITS | This section holds information defined by the program, whose format and meaning are determined solely by the program. |
| SHT_SYMTAB | This section holds a symbol table. Typically, SHT_SYMTAB provides symbols for link editing, though it may also be used for dynamic linking. As a complete symbol table, it may contain many symbols unnecessary for dynamic linking. An object file can also contain a SHT_DYNSYM section. |
| SHT_STRTAB | This section holds a string table. An object file may have multiple string table sections. |
| SHT_RELA | This section holds relocation entries with explicit addends, such as type Elf32_Rela for the 32-bit class of object files. An object may have multiple relocation sections. |
| SHT_HASH | This section holds a symbol hash table. An object participating in dynamic linking must contain a symbol hash table. An object file may have only one hash table. |
| SHT_DYNAMIC | This section holds information for dynamic linking. An object file may have only one dynamic section. |
| SHT_NOTE | This section holds notes (ElfN_Nhdr). |
| SHT_NOBITS | A section of this type occupies no space in the file but otherwise resembles SHT_PROGBITS. Although this section contains no bytes, the sh_offset member contains the conceptual file offset. |
| SHT_REL | This section holds relocation offsets without explicit addends, such as type Elf32_Rel for the 32-bit class of object files. An object file may have multiple relocation sections. |
| SHT_SHLIB | This section is reserved but has unspecified semantics. |
| SHT_DYNSYM | This section holds a minimal set of dynamic linking symbols. An object file can also contain a SHT_SYMTAB section. |
| SHT_LOPROC, SHT_HIPROC | Values in the inclusive range [SHT_LOPROC, SHT_HIPROC] are reserved for processor-specific semantics. |
| SHT_LOUSER | This value specifies the lower bound of the range of indices reserved for application programs. |
| SHT_HIUSER | This value specifies the upper bound of the range of indices reserved for application programs. Section types between SHT_LOUSER and SHT_HIUSER may be used by the application, without conflicting with current or future system-defined section types. |
字符串表和符号表(String and symbol tables)
存放scetion的名字,以及符号信息。其他结构通过index访问此结构中的字符串信息。符号表保存了用于定位符号引用的信息。它是以下结构的数组:
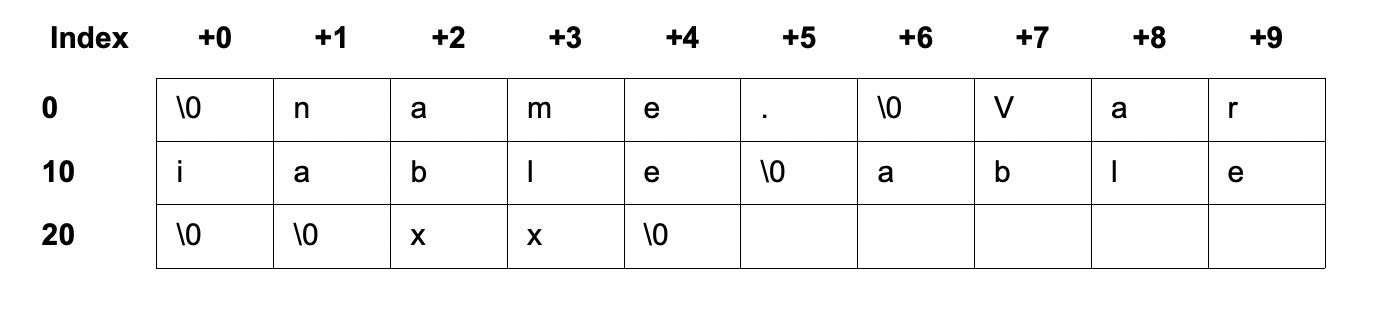
1 | typedef struct { |
Relocation entries (Rel & Rela)
重定位是连接符号引用(函数的名字)和符号定义(函数的定义、函数的实现)的过程。重定位文件必须包含如何修改section内容的信息,来让执行文件或共享目标文件正确的调用外部函数。
1 | typedef struct { |
r_offset:
对于重定位文件来说,此值表示从section的开始到被修改值在section中的偏移量。
对于执行文件和共享库文件来说,此值表示需要被重定位的虚拟地址。
r_info:
符号表的index和重定位的类型。
r_addend:
用于计算重定位字段的值。
Dynamic tags(Dyn)
.dynamic这个section存储一些包含动态链接信息的结构
1 | typedef struct { |
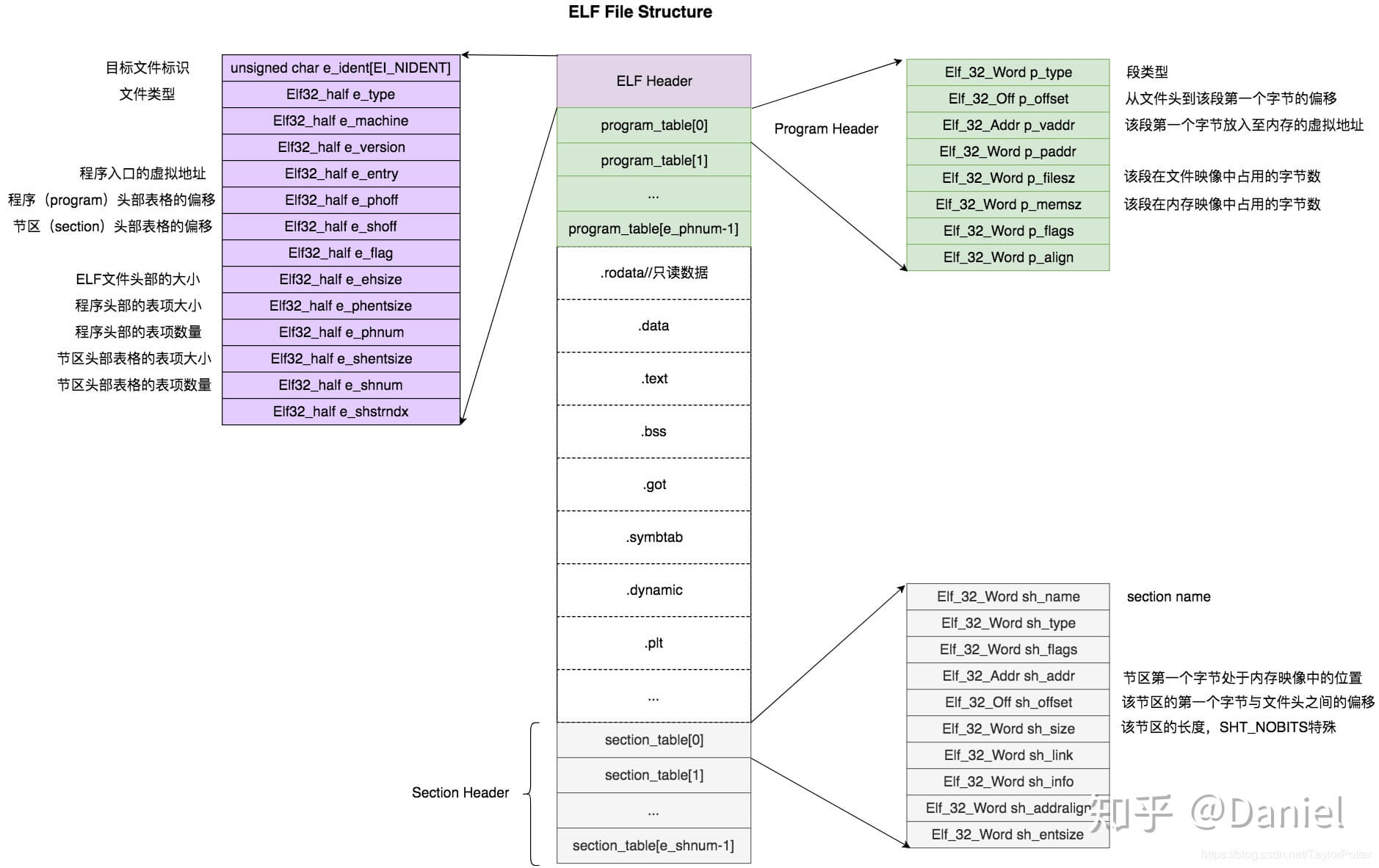
一些图示
三、参考链接
Linux manual page
The structure of an ARM ELF image
Compiling, Linking and Building