一、概述
Android中的视图是以树的形式组织起来的,它是一种层次结构。在代码中体现为组合模式,一个ViewGroup可以包含一个或多个View,同时ViewGroup又是一个View。在布局文件中体现为xml的结点和缩进。
同时视图的渲染少不了对其进行遍历,这就涉及数据结构中树的深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历。有时候一些复杂的布局一次遍历还无法完全确定View的信息。如何通过算法方式降低树的层次呢?也许这就是约束布局存在的意义吧。
在Android中,灵活运用ConstraintLayout包括以下几个点:
- 主属性
- 通过相对位置约束View
- 控制约束之间的距离
- 居中和偏移百分比
- 通过圆定位📌View
- 通过可见性控制View
- 通过分辨率约束View
- 通过链⛓约束View
- 辅助工具
- Barrier屏障约束
- Group分组约束
- Placeholder占位约束
- Guideline引导线约束
二、使用
2.1 通过相对位置约束View
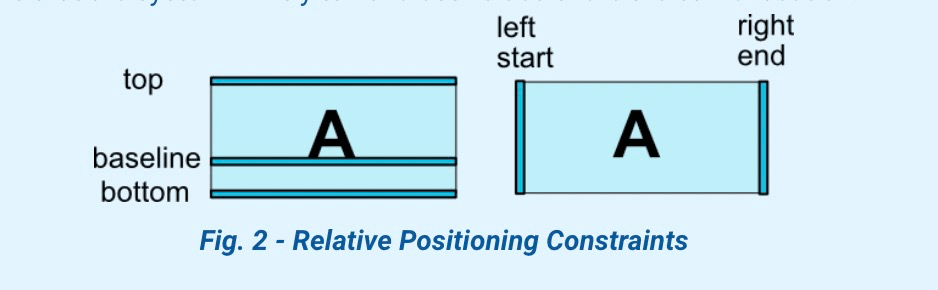
| 约束属性 |
描述 |
约束属性 |
描述 |
| layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf |
|
layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf |
|
| layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf |
|
layout_constraintRight_toRightOf |
|
| layout_constraintTop_toTopOf |
|
layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf |
|
| layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf |
|
layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf |
|
| layout_constraintStart_toEndOf |
|
layout_constraintStart_toStartOf |
|
| layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf |
|
layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf |
|
| layout_constraintBaseline_toBaselineOf |
|
|
|
2.2 控制约束之间的距离
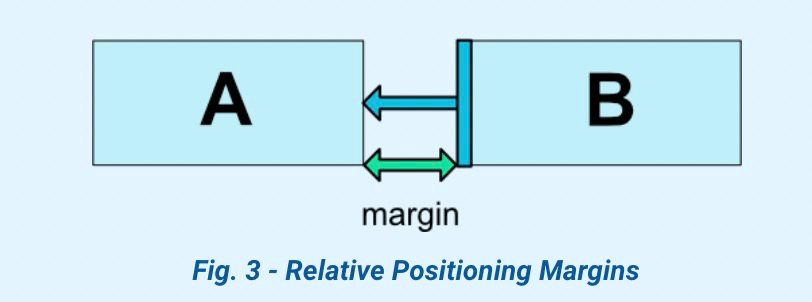
| 约束属性 |
描述 |
约束属性 |
描述 |
| android:layout_marginStart |
|
layout_goneMarginStart |
|
| android:layout_marginEnd |
|
layout_goneMarginEnd |
|
| android:layout_marginLeft |
|
layout_goneMarginLeft |
|
| android:layout_marginTop |
|
layout_goneMarginTop |
|
| android:layout_marginRight |
|
layout_goneMarginRight |
|
| android:layout_marginBottom |
|
layout_goneMarginBottom |
|
| android:layout_marginBaseline |
|
layout_goneMarginBaseline |
|
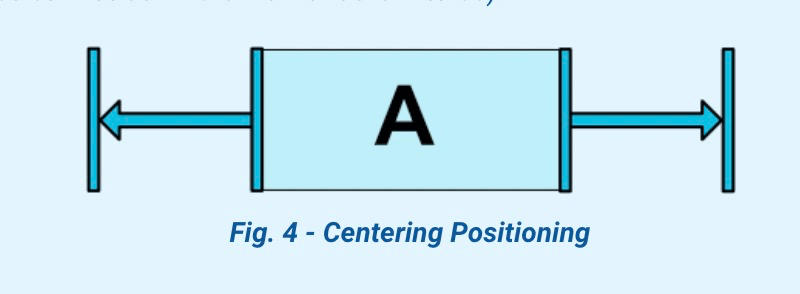
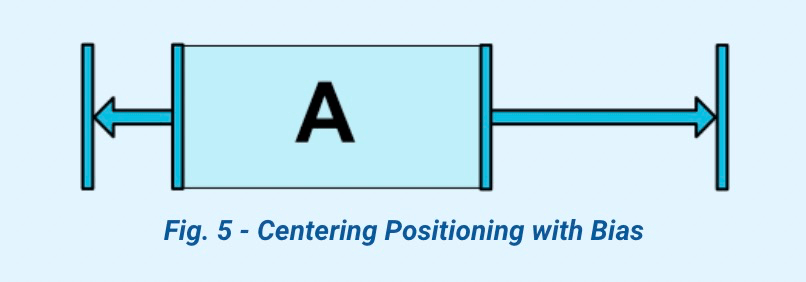
2.3 居中和偏移百分比
| 约束属性 |
描述 |
约束属性 |
描述 |
| layout_constraintHorizontal_bias |
|
layout_constraintVertical_bias |
|
2.4 通过圆定位📌View
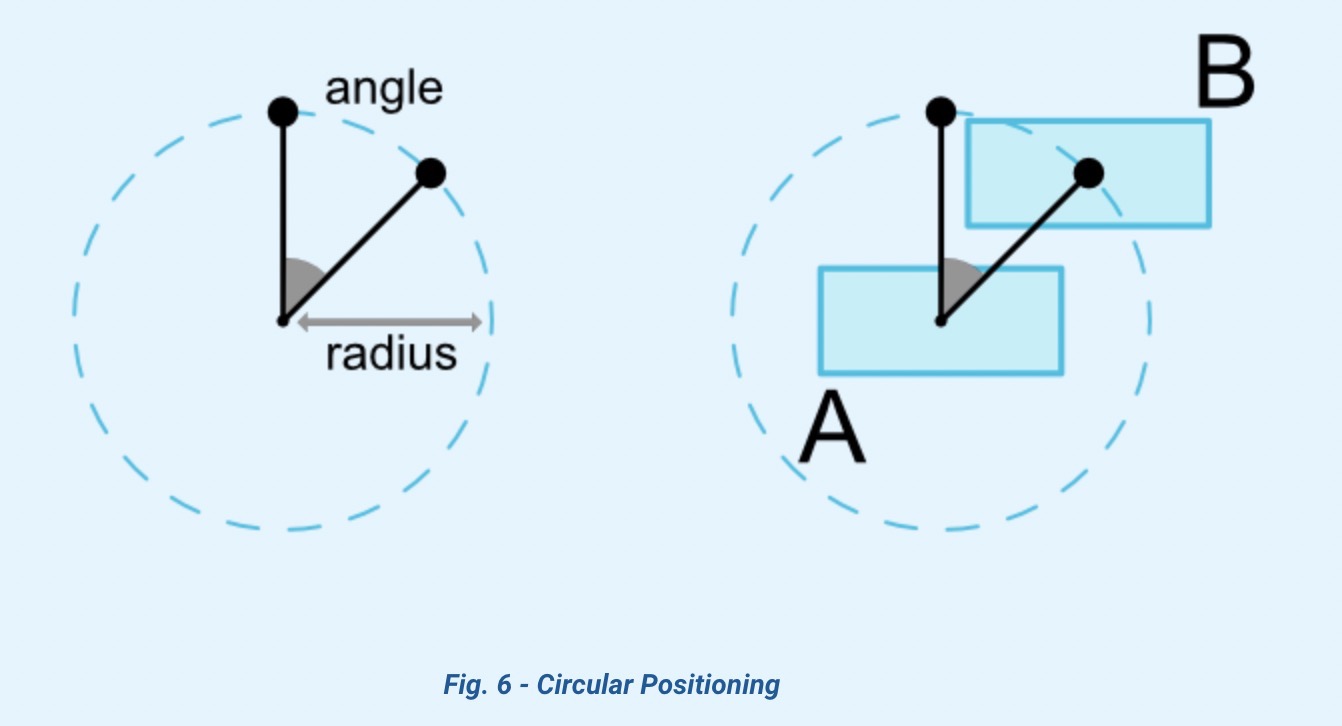
| 约束属性 |
描述 |
| layout_constraintCircle |
另一个widget的id |
| layout_constraintCircleRadius |
圆的半径 |
| layout_constraintCircleAngle |
角度 |
1
2
3
4
| <Button android:id="@+id/buttonB"
app:layout_constraintCircle="@+id/buttonA"
app:layout_constraintCircleRadius="100dp"
app:layout_constraintCircleAngle="45" />
|
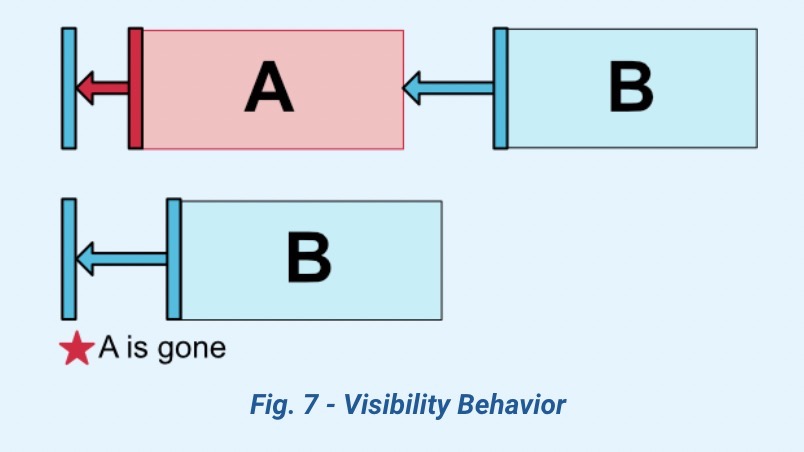
2.5 通过可见性控制View
2.6 通过分辨率约束View
| 约束属性 |
描述 |
约束属性 |
描述 |
| android:minWidth |
|
android:minHeight |
|
| android:maxWidth |
|
android:maxHeight |
|
2.6.1 百分比
1
2
3
4
5
| <Button android:id="@+id/buttonA"
android:layout_width="0dp"
app:layout_constraintWidth_default="percent"
app:layout_constraintWidth_percent="0.5"
/>
|
app:layout_constraintWidth_default可以取的值包括:
在ConstraintLayout-1.1之后,使用app:layout_constrainedWidth="true"替代app:layout_constraintWidth_default="wrap"
2.6.2 比率
宽高一比一:
1
2
3
4
| <Button android:id="@+id/buttonA"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="1:1"
/>
|
指定一条边符合约束比率:
1
2
3
4
5
| <Button android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintDimensionRatio="H,16:9"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"/>
|
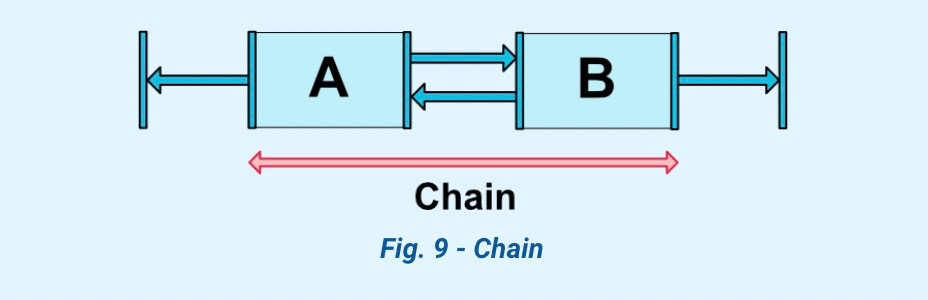
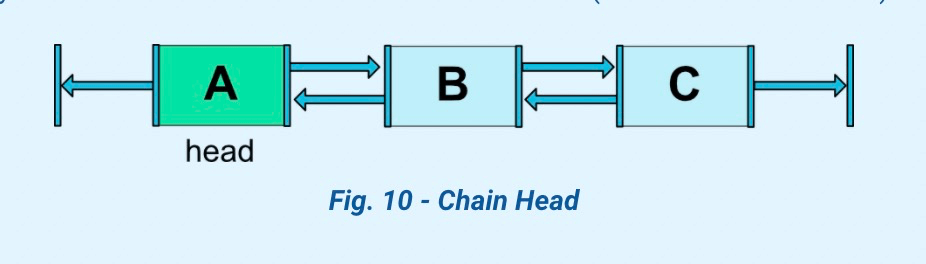
2.7 通过链⛓约束View
| 图示 |
Style |
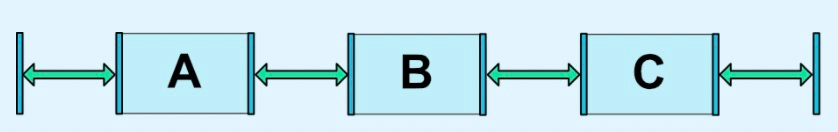 |
_chainStyle="spread" |
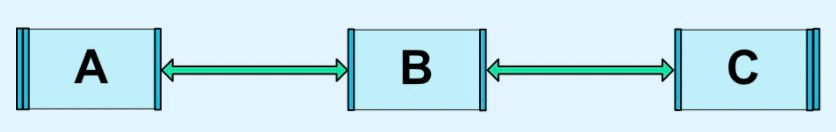 |
_chainStyle="spread_inside" |
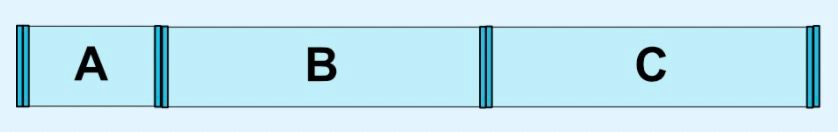 |
_chainStyle="spread"
_weight="1" |
 |
_chainStyle="packed" |
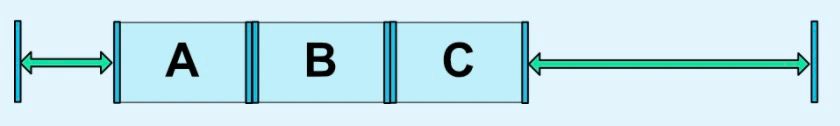 |
_chainStyle="packed"
_bias="0.3" |
2.8 Barrier
将多个View的某一边的极端值作为约束:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Barrier
android:id="@+id/barrier"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:barrierDirection="start/end"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="button1,button2" />
|
2.9 Group分组约束
将多个View作为一个组一起控制:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Group
android:id="@+id/group"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="visible"
app:constraint_referenced_ids="button4,button9" />
|
- 无法通过group设置点击事件
1
2
3
4
5
| group.referencedIds.forEach { id ->
view.findViewById(id).setOnClickListener {
}
}
|
2.10 Placeholder占位约束
Placeholder是一个虚拟的占位符View,界面上其他存在的View可以通过placeholder.setContentId(R.id.xxx)将自己的位置设置到placeholder的位置,原位置视图将不可见。
我们可以使用Placeholder搭建一个布局模板,include到其他布局当中,来填充模板中的视图,这将使所有的界面有一个通用的模板。
2.11 Guideline引导线约束
Guideline只能在ConstraintLayout中使用,在水平或垂直方向设置辅助布局的不可见线条。
| 约束属性 |
描述 |
| layout_constraintGuide_begin |
距布局的左边或者上边x处设置引导线 |
| layout_constraintGuide_end |
距布局右边或下面x处设置引导线 |
| layout_constraintGuide_percent |
宽或高的百分之x处设置引导线 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/guideline"
app:layout_constraintGuide_begin="100dp"
android:orientation="vertical"/>
<Button
android:text="Button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="@+id/guideline"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
|
三、原理
3.1 解决约束问题
3.1.1 定义变量
3.1.2 定义约束问题:
1
2
3
| a[1]x[1] + ... + a[n]x[n] = b
a[1]x[1] + ... + a[n]x[n] <= b
a[1]x[1] + ... + a[n]x[n] >= b
|
3.2.3 计算约束方程
食火鸡算法:食火鸡是一种生活在新几内亚热带雨林中的鸟类,以水果为食。同时它也是一种解决线性方程和线性不等式的算法。1990年在华盛顿大学被证明和发现。线性方程非常适合用于表示用户界面中视图的位置、大小、与其他视图的关系。
3.2 个人理解:
定义变量 -> 声明View对象
定义约束问题 -> 建立View之间的约束关系
计算约束方程 -> 计算视图的大小、坐标
四、参考文档
1.官方文档
2.基本使用
3.基本使用-译文
4.ConstraintLayout, Inside and Out: Part 1
5.ConstraintLayout, Inside and Out: Part 2
6.线性约束解决算法
7.解决约束