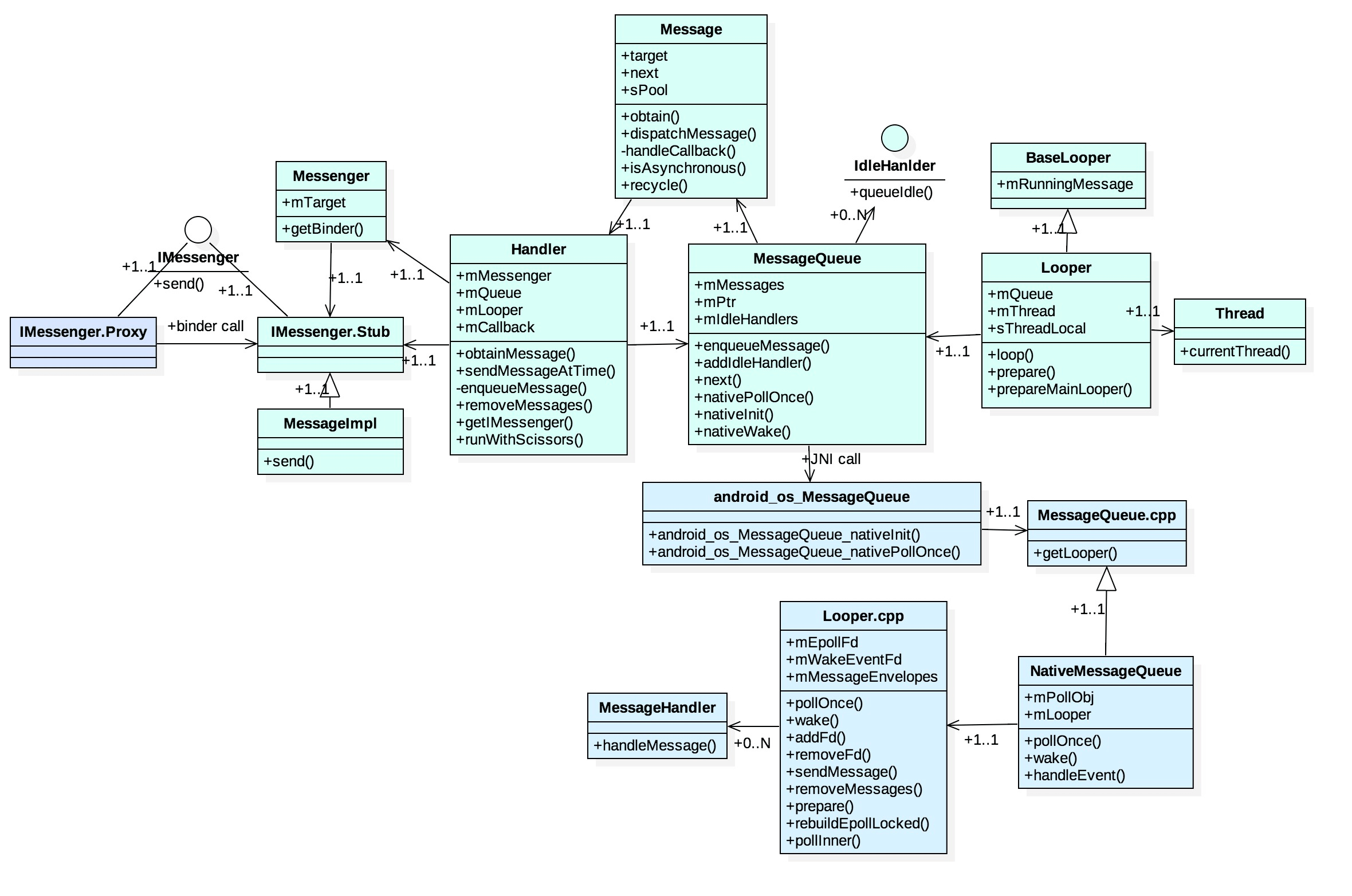
一、相关类和结构
二、基本使用
2.1 主线程的事件循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package android.app;
public final class ActivityThread extends ClientTransactionHandler
implements ActivityThreadInternal {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
Looper.loop();
}
}
|
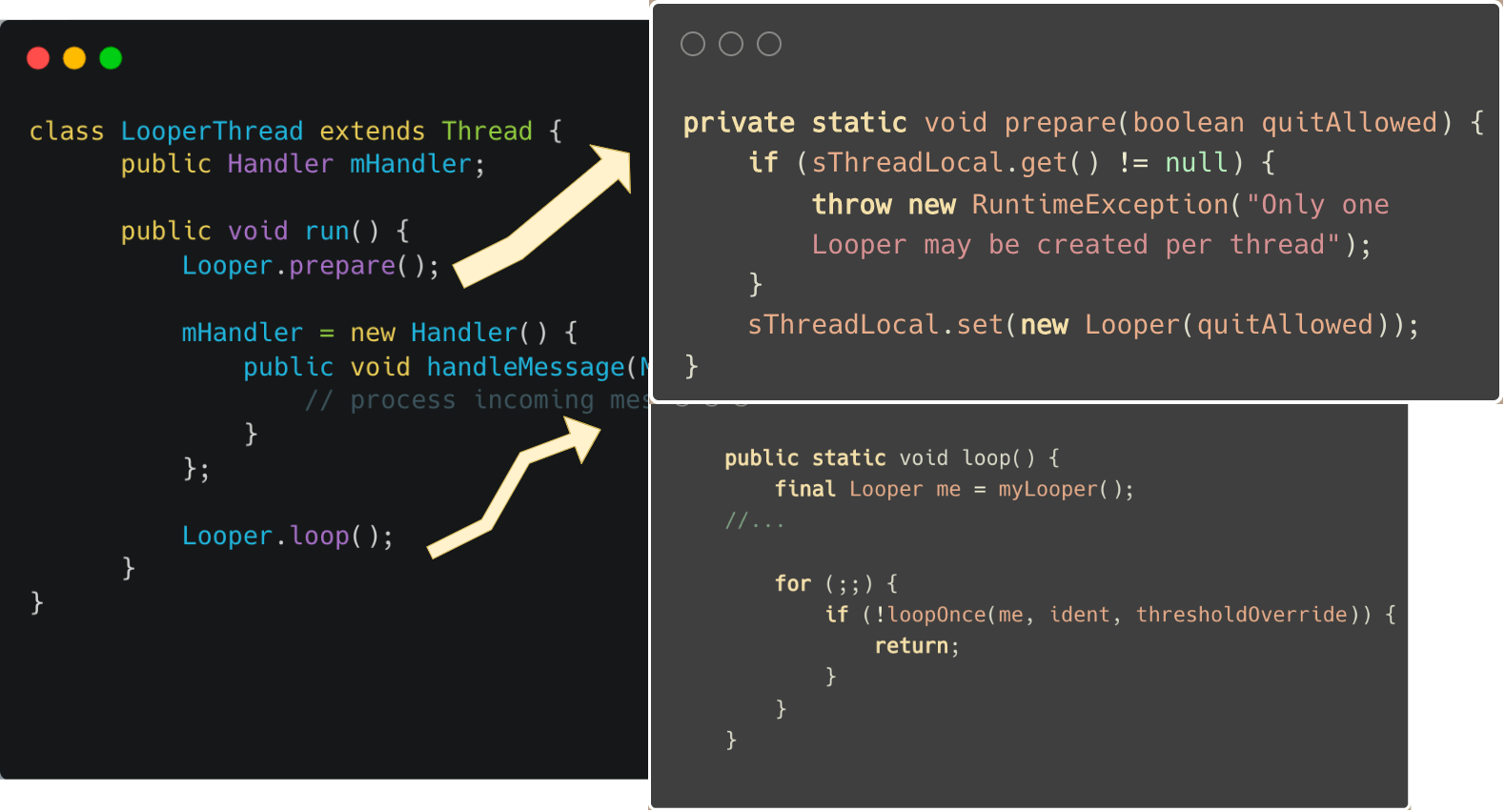
2.2 构建自己的事件循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class LooperThread extends Thread {
public Handler mHandler;
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler() {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}
|
三、原理剖析
3.1 构建事件循环
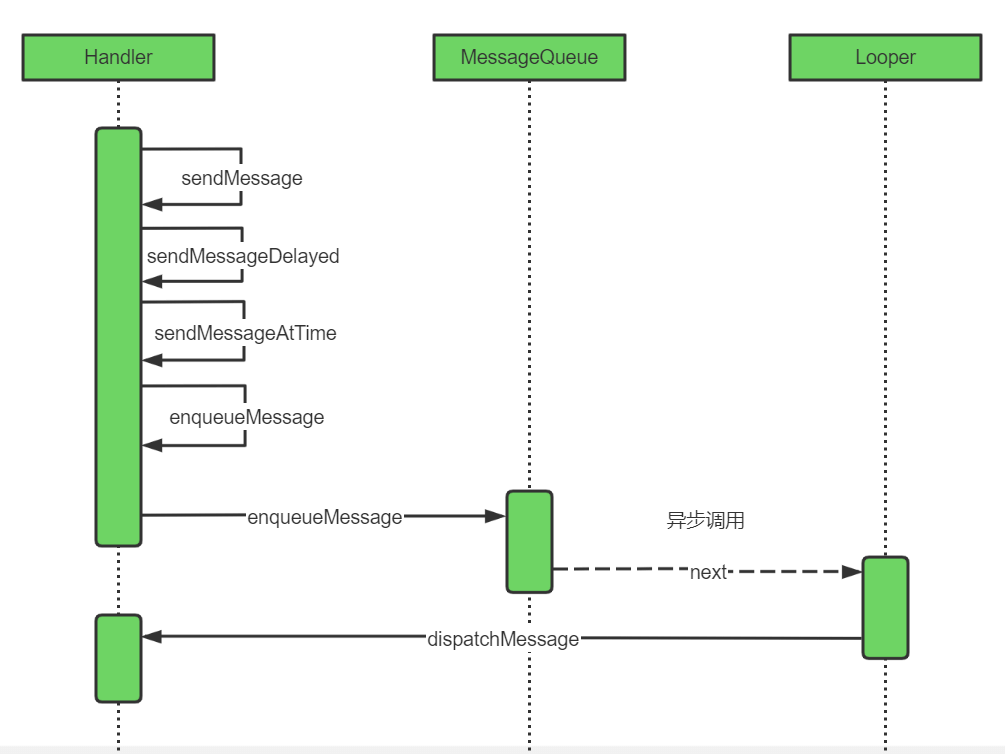
3.2 发送消息
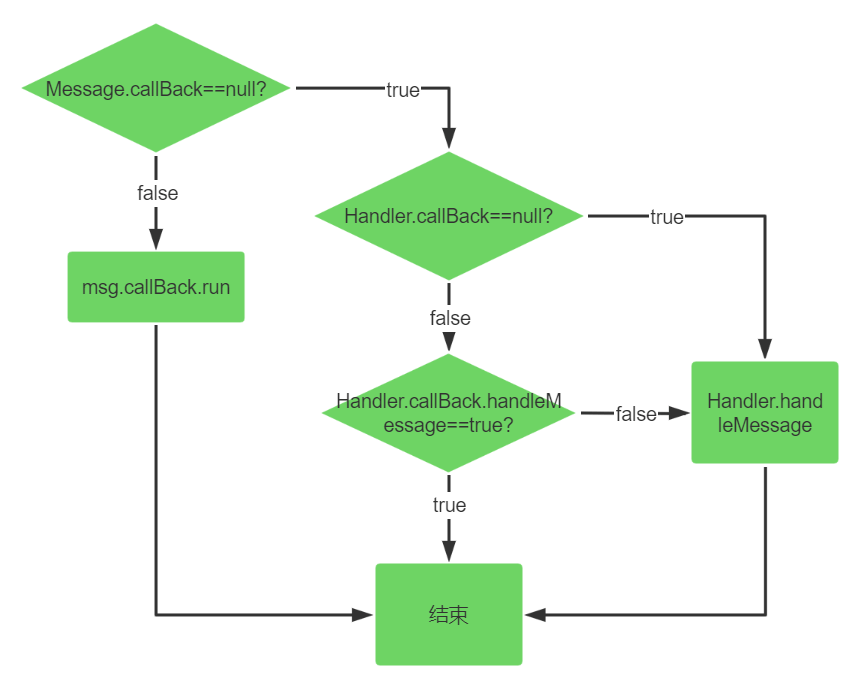
3.3 消息执行
3.4 同步屏障
3.4.1 消息的分类
3.4.2 同步屏障是什么
一种特殊的Message,其target=null
3.4.3 同步屏障工作原理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| Message next() {
int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1;
int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0;
for (;;) {
synchronized (this) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message prevMsg = null;
Message msg = mMessages;
if (msg != null && msg.target == null) {
do {
prevMsg = msg;
msg = msg.next;
} while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous());
}
if (msg != null) {
if (now < msg.when) {
} else {
mBlocked = false;
if (prevMsg != null) {
prevMsg.next = msg.next;
} else {
mMessages = msg.next;
}
msg.next = null;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Returning message: " + msg);
msg.markInUse();
return msg;
}
} else {
nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1;
}
}
}
}
|
当设置了同步屏障之后,next函数将会忽略所有的同步消息,返回异步消息。换句话说就是,设置了同步屏障之后,Handler只会处理异步消息。再换句话说,同步屏障为Handler消息机制增加了一种简单的优先级机制,异步消息的优先级要高于同步消息。
3.4.4 实际应用
Android应用框架中为了更快的响应UI刷新事件在ViewRootImpl.scheduleTraversals中使用了同步屏障
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInput();
}
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
|
四、其他
Epoll 实现原理
Linux select/poll机制原理分析



